Traffic Logs
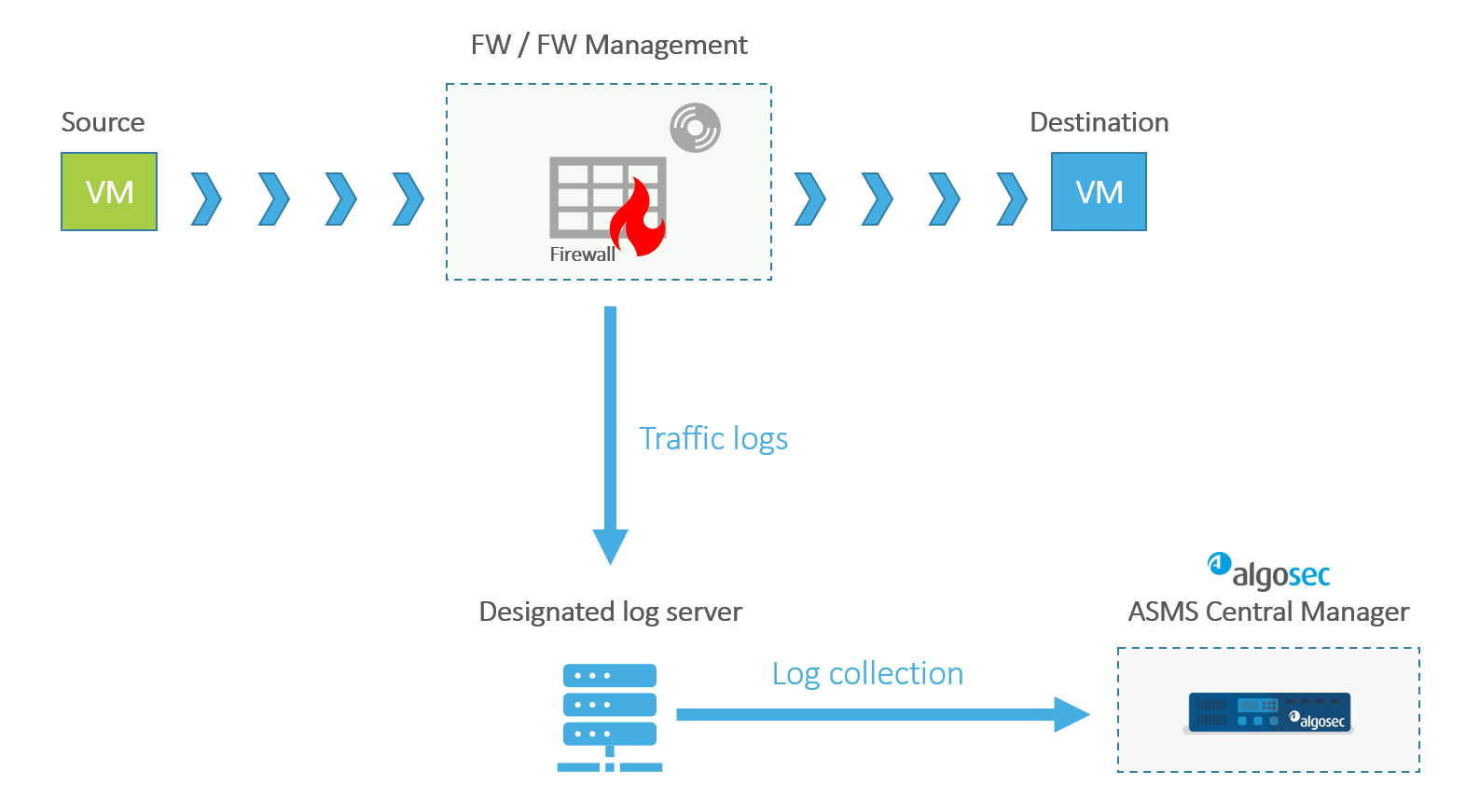
Incoming or outgoing traffic through a device is filtered by rules that either allow or disallow (deny) the traffic. For every event that is allowed or denied by a rule enabled for logging, a traffic log is written on the designated log server.
AFA collects the logs from the log server, processes them, crunches matching records, and writes the crunched records to the database tables. The traffic log information is used in AFA analysis and the Policy Optimization page of the report.
Traffic Logs and Policy Optimization
Depending on the Log Collection mode used (for example, standard, extensive, etc.), Policy Optimization analyzes the traffic log records for frequency of rule usage, exposing rules that are hardly used or never used.
The Policy Optimization rule recommendations displayed on the a device report's POLICY OPTIMIZATION page page use traffic logs to provide:
-
Suggestions for Rule Reordering
-
Rule usage statistics including -
-
Unused rules
-
Unused objects within rules
-
Least used rules
-
Most used rules
-
All rule usage (count, last date)
-
All NAT rule usage (count, last date)
-
Policy tuner analysis for all rules, including suggestions for tightening permissive rules
-
Troubleshooting Traffic Logs
Traffic logs are not present for the device
Do the following:
-
If there are no traffic logs for a particular device on the log server, check that there are rules on that device that are configured to send traffic logs.
-
Log into the designated ASMS log server and using dump, make sure that the server is receiving traffic logs in general.
Identifying Traffic Logs
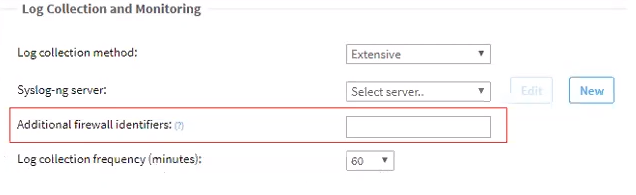
Sometimes additional identifiers are required in order to match between traffic logs and the device that generated them (as a result of load balancing or NAT, etc.). These identifiers must be added to the device configuration Log Collection and Monitoring section in Additional firewall identifiers field. When this field is updated in the device configuration, the device configuration on the log server will be updated.
Note: For devices with hierarchy, add these identifiers via the fwa.meta parameter of the device's meta file:
~/.fa/firewalls/<device name>/fwa.meta.
Audit Logs
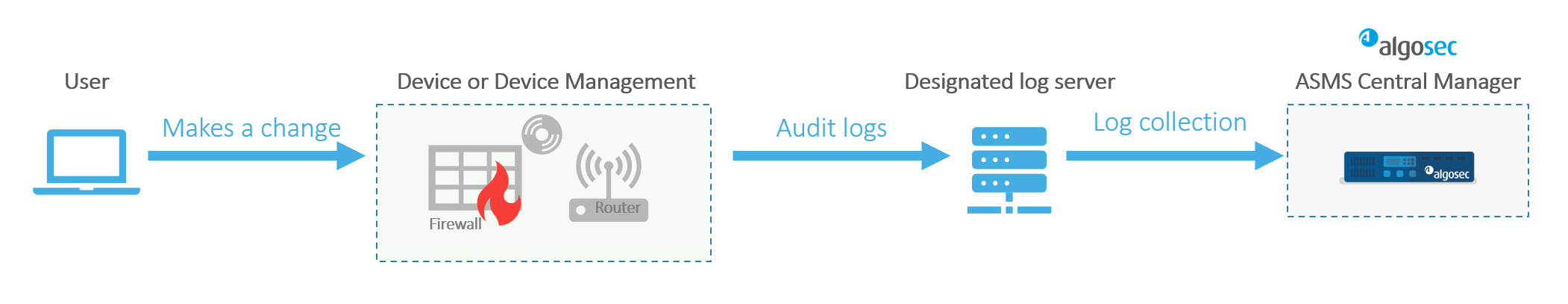
Having the latest information about each device enables optimal ASMS functionality. Audit logs hold the records of every change that was made on a device, providing:
-
What was the change
-
Who made the change
-
When was the change made
Each ASMS configured device continually stores its own configuration and change information, including an audit log for every new change.
Audit logs, produced each time a user makes a change to the configuration of a device, are collected by ASMS during both the Log Collection Process and the Monitoring Process . They feed the Changed by fields of the Changes page of the Report and the Changes tab for the device.
Working with the Audit Logs
Here are a few useful "tips" for working with Audit logs.
-
Audit logs record changes on ASMS configuration files. You can see and edit the list of monitored configuration files in /etc/audit/rules.d/audit.rules.
-
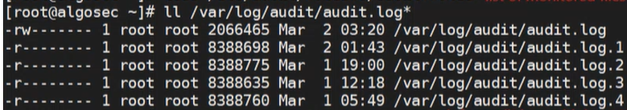
The Audit logs are saved in /var/log/audit/audit.log and similarly named files. Up to five files of up to 8 MB each are stored. Use the ll command to list them:
-
Use the ausearch command and the key value AlgoSec to filter for ASMS audit logs:
[root@algosec ~]# ausearch -k AlgoSec | less
Troubleshooting Audit Logs
The following can be signs of audit log misconfiguration:
-
No information in the Changed by column of the Changes tab
-
Log Collection status is red, indicating Log Collection failure
Do the following:
-
Check the Device Configuration to verify that the correct log server is configured and that this is the log server that Log Collection is querying.
-
See Algopedia articles that refer to audit log troubleshooting.