ASMS clusters prevent data loss and downtime in the event of hardware failures. Virtual Appliances and AlgoSec Hardware Appliances support both High Availability (HA) and Disaster Recovery (DR) clusters.
Note: If you have both ASMS deployed on virtual machines and also AlgoSec Hardware Appliances in your system, each cluster must have nodes of the same type: hardware-hardware or VM-VM.
Cluster roles and modes
Each appliance node in the cluster is assigned one of the following roles and service statuses:
| Roles |
|
| Service modes |
|
By default, the primary appliance is active, and the secondary appliance is in standby mode.
The primary and secondary appliances regularly verify that they can communicate with each other and that the other is alive. In the event that the primary appliance goes down, the secondary appliance will become active, in an event called failover.
ASMS clusters include the following types:
High Availability clusters
High Availability (HA) clusters both prevent downtime, protect data and improve performance as follows:
| Automatic failover |
A secondary appliance automatically becomes active if the primary appliance fails. Ping nodes are used to determine whether the primary appliance is connected to the network. If a ping to the node that represents the primary machine fails, the network connection on the primary appliance is considered to be down, triggering a failover to the secondary appliance. Note: Automatic failover occurs after a grace period of 15 minutes. Note: If you want to manually switch HA roles, see Manually switch appliance roles for HA. |
| Co-location |
Both nodes are located at the same site and are physically connected. This prevents a situation called split-brain, where failover might occur when the primary appliance is actually still active, such as if a ping from the primary appliance fails to reach the secondary appliance due to networking issues only. |
| Shared virtual IP address |
Configuring HA clusters includes configuring a virtual IP address shared by both machines. This ensures that if or when failover occurs, AlgoSec services remain available at the same IP address. |
| Database permissions |
In HA clusters, databases are fully active only on the secondary node, and partially active on the primary node. The secondary node also offers both read and write capabilities, while the primary node offers only read capabilities. In most cases, this does not affect your appliance configuration. |
| FireFlow separation | The resources of the secondary node of an HA cluster is used to run the FireFlow workload. The secondary machine functions as the primary FireFlow server, thus speeding up processes. Any FireFlow configurations (first or otherwise) need to be run on the FireFlow server. |
Post-failover scenarios
After failover occurs, the original secondary node becomes the new primary node.
- If the original primary node comes back online within 12 hours, it remains in the cluster as the new secondary node.
- Otherwise, the original primary node is removed from the cluster, and the original secondary node remains in the cluster as a single node.
For example:
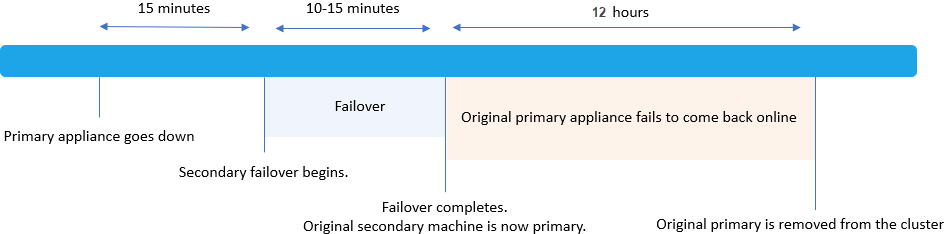
-
After failover, both FireFlow and ASMS will be on the same primary node. To restore FireFlow separation, on the algosec-conf menu select option 13 HA/DR Setup and then select the option to Switch Roles.
Add FireFlow to your clusters
If FireFlow was not licensed and configured when your cluster was originally built, break and rebuild the cluster after adding FireFlow to your license and configuring it.
For details, see
Disaster Recovery clusters
Disaster Recovery (DR) clusters protect data only.
The appliance nodes are located at different sites. If a primary appliance fails, the secondary appliance must be put into active mode manually. This is called manual failover, or switching appliance modes.
After failover occurs:
-
If the original primary node comes back online within 12 hours, it remains in the cluster as the new secondary node.
-
Otherwise, the original primary node is removed from the cluster, and the original secondary node remains in the cluster as a single node.
For more details, see Manual Failover for DR.
â See also: