This section describes how to manage network objects in AppViz.
Manage network objects
Do any of the following:
- View an overview of all network objects and edit, clone, or delete them. For details, see Network object dashboard.
- View an overview of each network object. For details, see View a network object.
- Create new network objects. For details, see Add and edit network objects.
- View the applications that include a specific network object. For details, see Network objects applications.
- View the change requests that involve the network object. For details, see Network object change requests.
- View activity logs for a specific network object. For details, see Network object activity logs.
- Manage network object permissions using tags. For details, see Managing Object Permissions Using Tags
Note: If two device objects with the same name have different content, the device on which the objects were defines will be indicated throughout the Web Interface.
Tip: To return to the other areas available from the main menu, click the hamburger menu  at the top left, and select the page you want to navigate to.
at the top left, and select the page you want to navigate to.
Abstract objects
Network objects may be identified as abstract objects.
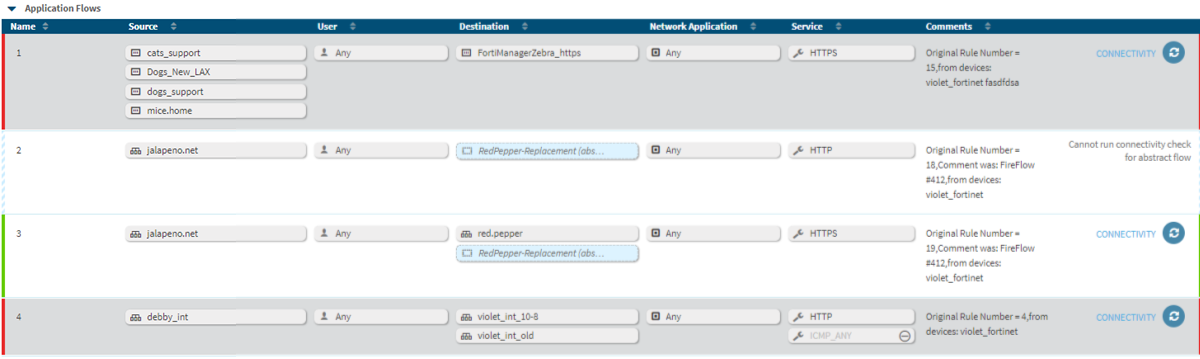
Abstract objects are network objects without defined content. You can use abstract objects to help you design an application flow before you know all the network details, such as type and IP address. Abstract objects appear in pale blue and with (abstract) after their name in flows and in the application diagram.
Change requests are not created when you add an abstract object to a flow because the object does not represent a change in the traffic required for the application. If a flow in an application has only an abstract object for either the source or destination field, the flow itself is abstract. It does not represent real traffic, so you cannot run a connectivity check on the flow. These flows are indicated with a pale blue border and striped connectivity indicator.
At any point, you can update the abstract object with actual values, and the object will be identified as a regular network object. For details, see Network object dashboard.