Threat Management
This page explains how to manage threats using Mitigation Rules in AppViz Cloud App Analyzer.
Mitigation Rules are used by the CI pipeline in GitHub and the CD pipeline in AWS ECR (Elastic Container Registry) and Azure Container Registry (CR) and GCP Artifact registry (AR) to determine if container images should be flagged as high-risk.
By scanning container images both statically and dynamically, Cloud App Analyzer ensures comprehensive coverage against a wide range of security threats. Cloud App Analyzer detonates the containers to analyze their behavior dynamically across different behavioral characteristics like IP addresses, Domains, Countries and Open Ports. Static scanning includes the detection of any malware and vulnerabilities within images.
Cloud App Analyzer classifies rules into six different classes of artifact types.
The built-in default lists of Mitigation Rules that Cloud App Analyzer uses are collected from a number of sources including the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), US government databases, the OECD, other public websites, and the ClamAV engine, updated daily.
The default values of the artifact rules include the artifact item and its risk severity level. You can define the minimum risk-level Cloud App Analyzer will use to block pull requests (in the CI pipeline in GitHub) and to lock repositories (in the CD pipeline). For example, when the minimum risk-level is set to high in CI/CD Container Security, an IP address defined as medium-level risk in Mitigation Rules will not be blocked in a GitHub pull request. However, if the minimum risk-level is set to medium in CI/CD Container Security, an IP address that is defined as a medium-level risk in Mitigation Rules will be blocked in a GitHub pull request.
You can adjust default individual mitigation rules to meet your specific use case by maintaining a Custom Blocklist to extend the existing Default (Block)lists or by using a Default Allowlist to override definitions in the Default (Block)lists.
-
For more information about the CI pipeline in GitHub and to set minimum risk-level, see Cloud App Analyzer CI/CD Container Security.
-
For more information about the CD pipeline and to set minimum risk-level, see:
- For AWS ECR: Enable Threat Management on AWS ECR
-
For Azure ACR: Enable Threat Management on Azure ACR
-
For GCP AR: Enable Threat Management on GCP AR
Accessing Mitigation Rules
To access the list of mitigation rules for each artifact type:
Do the following:
Below is a technical rundown of the six categories of artifacts that Cloud App Analyzer monitors. The first four artifacts are dynamic and the last two are static:
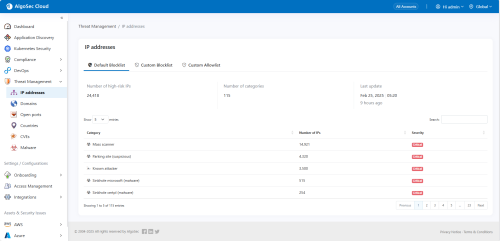
IP Addresses
The following details IP address rules management, including how Cloud App Analyzer identifies and responds to IP address-related threats in CI/CD environments.
|
Details |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Scanning Action |
Cloud App Analyzer scans for attempts to connect to high-risk remote IPs.* |
|
Analysis type |
Dynamic |
|
CI Blocking Mechanism |
If a container attempts to connect to a high-risk IP address, Cloud App Analyzer will block the GitHub pull request before that container is deployed into the production environment. |
|
CD Protection Strategy |
Cloud App Analyzer scans containers pushed to AWS ECR and will block those with high-risk characteristics, to prevent them from entering the production environment. |
|
Default Blocklist |
Cloud App Analyzer generates a fresh list daily of almost 30,000 high-risk IP addresses across more than 100 categories known to be associated with malicious activities. |
|
Severities |
|
|
Custom Blocklist |
Customers can extend the Default Blocklist by adding specific IP addresses (or the CIDR notation of that IP address) they wish to block. |
|
Custom Allowlist |
Customers can allow IP addresses (or the CIDR notation of that IP address), preventing these from being flagged by Cloud App Analyzer as high-risk. |
* Cloud App Analyzer will block pull requests (in the CI pipeline in GitHub) and to lock repositories (in the CD pipeline) based on user-defined minimum risk-levels.
Domains
The following details domains rules management, including Cloud App Analyzer identifies and responds to domain-related threats in CI/CD environments.
| Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Scanning Action | Cloud App Analyzer scans and analyzes if traffic is directed to known high-risk domains*. |
| Analysis type | Dynamic |
| CI Blocking Mechanism | When a container connects to a high-risk domain, Cloud App Analyzer blocks the related GitHub pull request to prevent deployment to production. |
| CD Protection Strategy | Containers pushed to AWS ECR are scanned for domain risks, and those with connections to high-risk domains can be blocked by Cloud App Analyzer to prevent it from entering the production environment. |
| Default Blocklist | Cloud App Analyzer compiles a fresh list daily of over half a million high-risk domains across more than 2000 categories. |
| Severities |
Domains are categorized by risk level, with a vast array of categories to cover the spectrum of internet-based threats.
|
| Custom Blocklist | You can personalize the Default Blocklist by adding domains you specifically want to block. |
| Custom Allowlist | You can create exceptions by adding domains to the Custom Allowlist, preventing those domains from being flagged as high-risk. |
* Cloud App Analyzer will block pull requests (in the CI pipeline in GitHub) and to lock repositories (in the CD pipeline) based on user-defined minimum risk-levels.
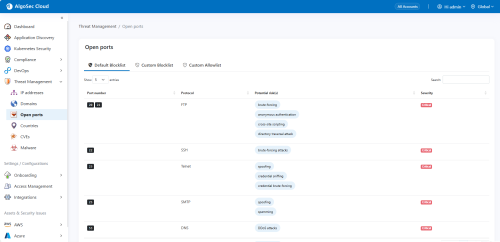
Open Ports
The following details Open Ports rules management, including Cloud App Analyzer identifies and responds to Open Ports-related threats in CI/CD environments.
| Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Scanning Action | Cloud App Analyzer checks for open ports that could expose vulnerabilities.* |
| Analysis type | Dynamic |
| Database Source | |
| CI Blocking Mechanism | If a container has high-risk ports open, Cloud App Analyzer will block the associated GitHub pull request to prevent CI deployment. |
| CD Protection Strategy | If high-risk open ports are detected, Cloud App Analyzer will block the container's delivery to AWS ECR to prevent it from entering the production environment. |
| Default Blocklist | Cloud App Analyzer maintains a list of high-risk ports known to introduce vulnerabilities within containers. Updated daily. |
| Severities |
Ports in the Default Blocklist are considered critical vulnerabilities that require immediate attention and are blocked to protect the container's security.
|
| Custom Blocklist | Users can add to the Default Blocklist by specifying additional ports they want to block based on their security policies or risk assessments. |
| Custom Allowlist | Users can override the Default Blocklist by adding ports to the Custom Allowlist if they are necessary for their operations and are not considered a security risk. |
* Cloud App Analyzer will block pull requests (in the CI pipeline in GitHub) and to lock repositories (in the CD pipeline) based on user-defined minimum risk-levels.
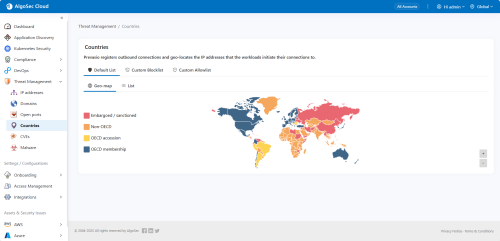
Countries
Cloud App Analyzer manages geographical IP address risks associated with container traffic, offering a framework for users to adapt security measures based on country risk assessments and specific operational needs.
| Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Scanning Action | Cloud App Analyzer checks container traffic to determine if the geographical location of an IP is a potential risk.* |
| Analysis Type | Dynamic |
| Database Source | US government published lists on embargoed countries. OECD info comes from OECD website. |
| CI Blocking Mechanism | Blocks containers during CI if they communicate with high-risk countries. |
| CD Protection Strategy | Blocks deployment of containers in the CD phase if they are associated with high-risk countries. |
| Default List |
Countries are categorized by OECD status and risk level, indicating allowed and blocked connections. Updated daily.
|
| Severities |
|
| Custom Blocklist | Users can add countries to block that are not included in the Default List. |
| Custom Allowlist | Users can allow countries to prevent them from being blocked, overriding the Default List settings. |
* Cloud App Analyzer will block pull requests (in the CI pipeline in GitHub) and to lock repositories (in the CD pipeline) based on user-defined minimum risk-levels.
CVEs
The following details CVEs rules management, including how Cloud App Analyzer identifies and responds to CVE-related threats in CI/CD environments.
| Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Scanning Action | Cloud App Analyzer identifies and assesses vulnerabilities in containers, focusing on known exploitable CVEs.* |
| Analysis Type | Static |
| Source | Open source databases and US government (CISA) database of known exploited vulnerabilities |
| CI Blocking Mechanism | Cloud App Analyzer blocks the GitHub pull request if a container has known exploitable vulnerabilities. |
| CD Protection Strategy | Blocks the deployment of containers into the AWS ECR if they contain exploitable vulnerabilities. |
| Default Blocklist | Compiled daily, this list includes CVEs that are currently being exploited in the wild. Updated daily. |
| Severities | Known exploited vulnerabilities are prioritized; CVEs that are critical but not exploited may not result in blocking. |
| Custom Blocklist | Users can add CVEs to this list to ensure containers with these vulnerabilities are blocked, extending the coverage beyond the default list. |
| Custom Allowlist | Users have the option to allow CVEs, preventing them from triggering a block if they believe the vulnerability does not pose a risk in their specific context. |
* Cloud App Analyzer will block pull requests (in the CI pipeline in GitHub) and to lock repositories (in the CD pipeline) based on user-defined minimum risk-levels.
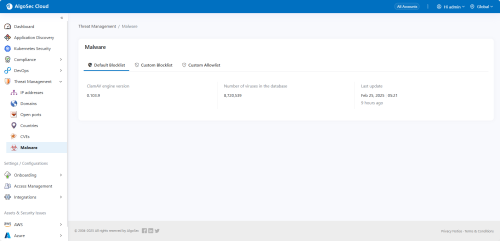
Malware names
The following details malware rules management, including how Cloud App Analyzer identifies and responds to malware-related threats in CI/CD environments.
| Details | Description |
|---|---|
| Scanning Action | Cloud App Analyzer scans Docker container files for malware using the ClamAV engine.* |
| Analysis Type | Static |
| Source | ClamAV engine |
| CI Blocking Mechanism | Cloud App Analyzer blocks the GitHub pull request if high-risk malware is detected in the container. |
| CD Protection Strategy | Blocks the deployment of containers into the AWS ECR if they contain high-risk malware. |
| Default Blocklist |
Uses ClamAV's database to detect malware, adware, corrupted files, and EICAR test files within containers. Updated daily.
|
| Severities |
|
| Custom Blocklist | Users can customize this list to block additional malware names that they are concerned about. |
| Custom Allowlist | Users can allow certain malware names if they believe they do not pose a risk in their specific context or for files like EICAR test files. |
* Cloud App Analyzer will block pull requests (in the CI pipeline in GitHub) and to lock repositories (in the CD pipeline) based on user-defined minimum risk-levels.
Custom Blocklists
The Threat Management page for each artifact type contains three tabs:
-
Default (Block)list: Contains a built-in set of threat management rule-sets.
-
Custom Blocklist: You can extend Default (Block)list by adding your own custom definitions.
-
Custom Allowlist: Override the Default (Block)list by adding your own custom definitions
Adding IPs to the Custom Blocklist
To extend your network’s security by adding definitions to the Custom Blocklist, follow these steps:
-
Click on Threat Management in the left menu. The list of artifacts open.
-
 For IP Addresses
For IP Addresses
-
Choose IP addresses from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Blocklist tab.
-
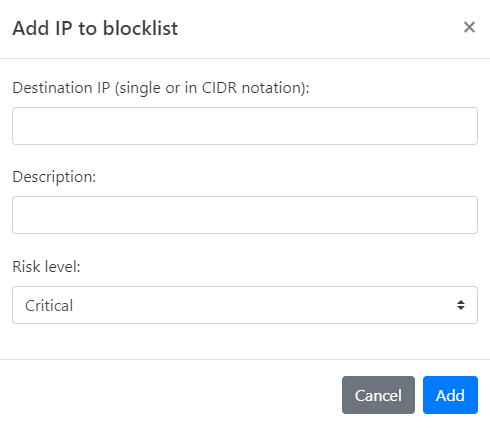
Click Add IP. The Add IP to blocklist dialog opens.
-
Enter the Destination IP you wish to block. This can be a single IP address or a range in CIDR notation.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the IP is being blocked.
-
Set the Risk Level, choosing from Critical, High, Medium, Low, or Informational.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this IP to your Custom Blocklist.
 For Domains
For Domains
-
Choose Domains from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Blocklist tab.
-
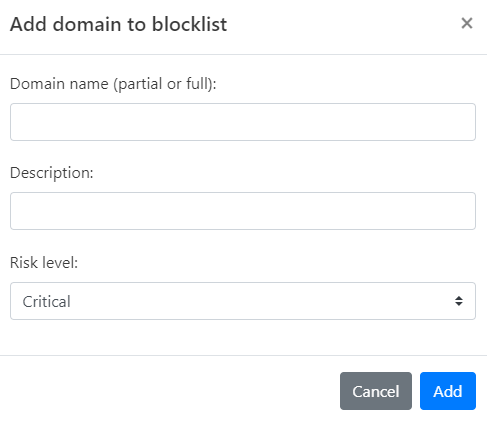
Click Add domain. The Add domain to blocklist dialog opens.
-
Enter the Domain name you wish to block.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the IP is being blocked.
-
Set the Risk Level, choosing from Critical, High, Medium, Low, or Informational.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this domain to your Custom Blocklist.
 For Open Ports
For Open Ports
-
Choose Open Ports from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Blocklist tab.
-
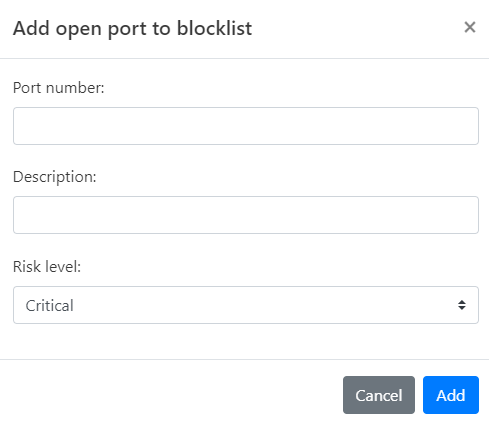
Click Add open port. The Add open port to blocklist dialog opens.
-
Enter the Port number you wish to block.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the port is being blocked.
-
Set the Risk Level, choosing from Critical, High, Medium, Low, or Informational.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this IP to your Custom Blocklist.
 For Countries
For Countries
-
Choose Open Ports from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Blocklist tab.
-
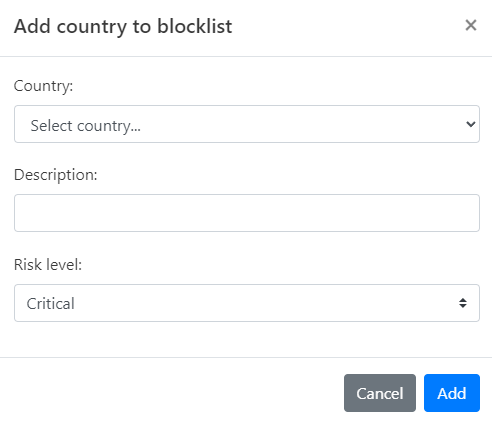
Click Add Countries. The Add Countries to blocklist dialog opens.
-
Select the Country you wish to block.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the country is being blocked.
-
Set the Risk Level to Critical.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this country to your Custom Blocklist.
 For CVEs
For CVEs
-
Choose CVEs from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Blocklist tab.
-
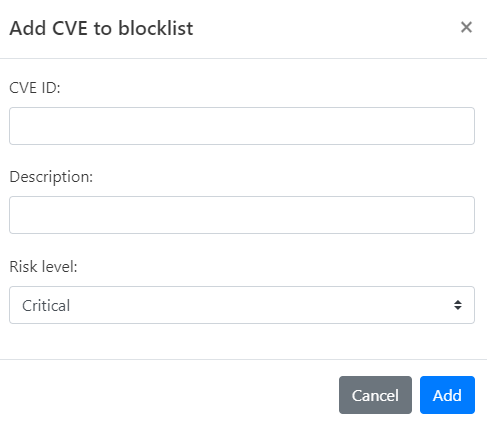
Click Add CVE. The Add CVE to blocklist dialog opens.
-
Enter the CVE ID you wish to block.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the IP is being blocked.
-
Set the Risk Level, choosing from Critical, High, Medium, Low, or Informational.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this CVE to your Custom Blocklist.
 For Malware names
For Malware names
-
Choose Malware names from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Blocklist tab.
-
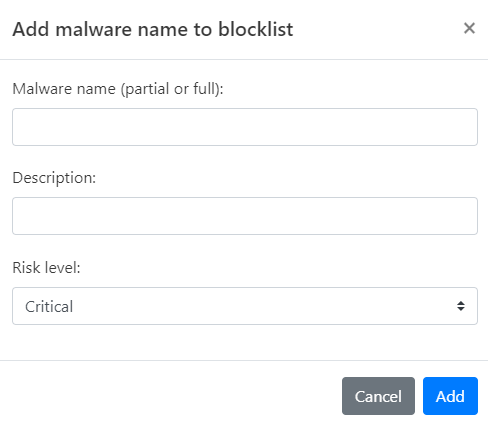
Click Add malware name. The Add malware name to blocklist dialog opens.
-
Enter the malware name you wish to block. This can be a whole or partial name.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the IP is being blocked.
-
Set the Risk Level, choosing from Critical, High, Medium, Low, or Informational.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this IP to your Custom Blocklist.
-
Adding IPs to the Custom Allowlist
If there are specific IP addresses that need uninterrupted access despite being on the Default Blocklist, you can add them to the Custom Allowlist.
To override default definitions to the Custom Blocklist, follow these steps:
-
Click on Threat Management in the left menu. The list of artifacts open.
-
 For IP Addresses
For IP Addresses
-
Choose IP addresses from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Allowlist tab.
-
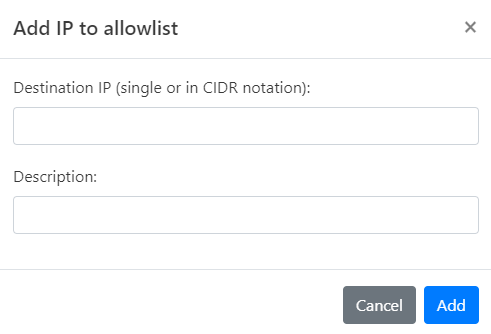
Click Add IP. The Add IP to Allowlist dialog opens.
-
Enter the Destination IP you wish to allow. This can be a single IP address or a range in CIDR notation.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the IP is being allowed.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this IP to your Custom Allowlist.
 For Domains
For Domains
-
Choose Domains from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Allowlist tab.
-
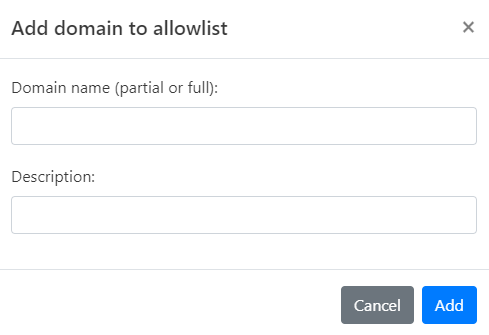
Click Add domain. The Add domain to Allowlist dialog opens.
-
Enter the Domain name you wish to allow.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the IP is being allowed.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this domain to your Custom Allowlist.
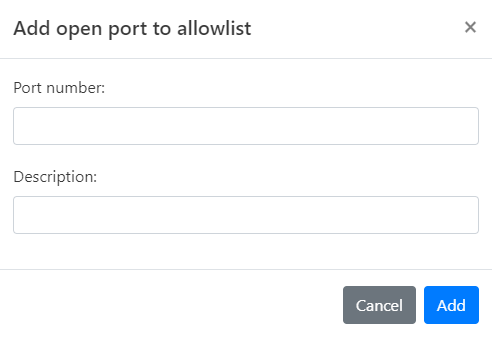
 For Open Ports
For Open Ports
-
Choose Open Ports from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Allowlist tab.
-
Click Add open port. The Add open port to Allowlist dialog opens.
-
Enter the Port number you wish to block.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the port is being allowed.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this IP to your Custom Allowlist.
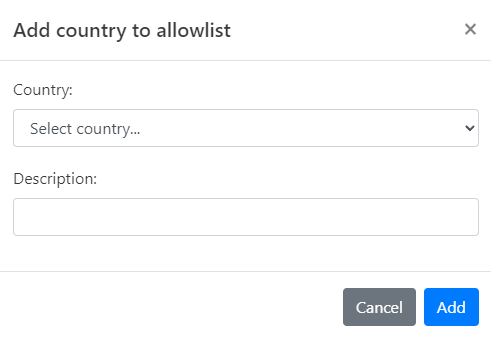
 For Countries
For Countries
-
Choose Open Ports from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Allowlist tab.
-
Click Add Countries. The Add Countries to Allowlist dialog opens.
-
Select the Country you wish to allow.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the country is being allowed.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this country to your Custom Allowlist.
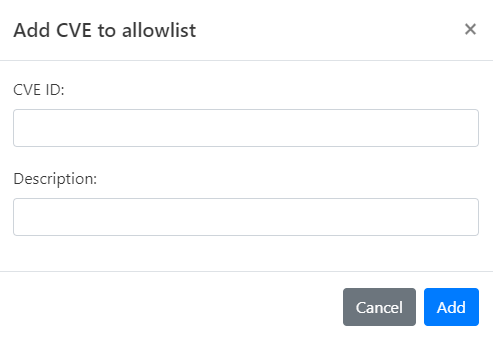
 For CVEs
For CVEs
-
Choose CVEs from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Allowlist tab.
-
Click Add CVE. The Add CVE to Allowlist dialog opens.
-
Enter the CVE ID you wish to allow.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the IP is being allowed.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this CVE to your Custom Allowlist.
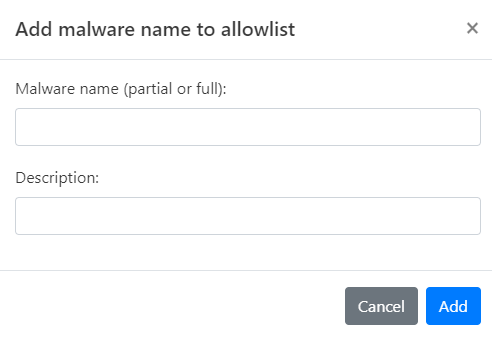
 For Malware names
For Malware names
-
Choose Malware names from the menu to open its page.
-
Select the Custom Allowlist tab.
-
Click Add malware name. The Add malware name to Allowlist dialog opens.
-
Enter the malware name you wish to allow. This can be a whole or partial name.
-
Provide a Description for this rule, explaining why the IP is being allowed.
-
Click Add to finalize the addition of this IP to your Custom Allowlist.
-